Today's June jobs report is being touted as strong enough to put any chance of a Fed ease on hold. That's silly, in my view. Putting things in the proper perspective, today's job report was one more in a year's worth of mediocre numbers. Private sector jobs (the ones that really count) have been growing at a 1% rate for over a year, which is consistent with real GDP growth of about 2%, a bit less than we've seen since 2010. Nothing in this report should give the Fed a reason to keep monetary policy tight.
Thursday, July 3, 2025
The June jobs report was not strong
Today's June jobs report is being touted as strong enough to put any chance of a Fed ease on hold. That's silly, in my view. Putting things in the proper perspective, today's job report was one more in a year's worth of mediocre numbers. Private sector jobs (the ones that really count) have been growing at a 1% rate for over a year, which is consistent with real GDP growth of about 2%, a bit less than we've seen since 2010. Nothing in this report should give the Fed a reason to keep monetary policy tight.
Friday, June 27, 2025
Big Picture charts: modest growth and low inflation
Here are 5 charts which illustrate some very important points about the state of the economy and the outlook for inflation.
The economy is doing "Ok", but it's nothing to write home about. The housing sector is struggling mightily, and is very unlikely to improve without a boost from lower interest rates. Jobs growth is modest at best, and unlikely to improve without immigration reform which prioritizes making hard-working illegals legal instead of deportable.
There is no longer any doubt that the Fed has tamed inflation.
Given low inflation and an economy that is struggling, there is no reason for the Fed to delay lowering interest rates. Trump is right to criticize Chairman Powell for this, but Trump could help by backing off on his egregious tariff demands and his aggressive deportations of illegals, most of whom are decent, hard-working, and tax-paying members of society. He should focus instead on lowering tax and regulatory burdens and greatly expanding immigration quotas.
Given low inflation and an economy that is struggling, there is no reason for the Fed to delay lowering interest rates. Trump is right to criticize Chairman Powell for this, but Trump could help by backing off on his egregious tariff demands and his aggressive deportations of illegals, most of whom are decent, hard-working, and tax-paying members of society. He should focus instead on lowering tax and regulatory burdens and greatly expanding immigration quotas.
Chart #1
Chart #1 is yet another update of a chart I've been featuring for the past 15 years. The green line represents the 3.1% annual growth path the economy followed from 1966 through 2007. During that time, the economy was able to rebound and regain that growth path after every recession (this is commonly referred to as the "plucked string" theory of growth). Since the end of the Great Recession in mid-2009, the economy has only managed to follow a 2.3% annual growth path (red line). If the economy had instead recovered to a 3.1% growth path it would be 23% bigger today. I've attributed this monstruous growth shortfall to increased tax and regulatory burdens and a sizable increase in transfer payments. (See my post from 11 years ago which explains this in greater detail.)
Chart #2
Chart #2 compares the year over year growth rate of private sector jobs (red line) with the year over year growth rate of real GDP (blue line). It stands to reason that without more people working it's hard for the economy to expand. Currently, jobs growth is only slightly higher than 1%, and the economy has expanded by only 2% in the past year. That 1% difference is a good approximation of productivity growth, which is less than the 1.9% annualized rate of productivity since 1966. If jobs growth doesn't pick up (and it won't if we are deporting millions of hard-working illegals), then the economy is going to continue to grow at a sluggish pace.
Chart #3
Chart #3 compares the level of housing starts (blue line) to an index of homebuilders' sentiment (red line). There is only one interpretation: the outlook for the housing market is gloomy. Housing affordability is at all-time lows (due to the combination of high prices and high interest rates), and the inventory of unsold homes is relatively high and rising rapidly. I'm hearing talk that construction sites around Southern California are having trouble getting workers to show up—they are mostly Mexican and many are likely illegally here. Everyone is afraid of ICE raids.
Chart #4
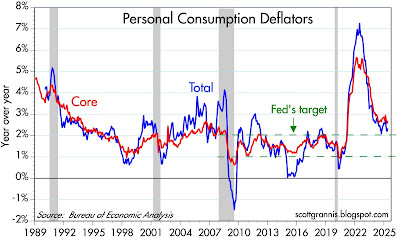
Chart #4 shows the year over year change in the Personal Consumption Deflators (total and core). Although both are somewhat above the Fed's target range, a closer looks says they are well within it. In the past three months (March, April, and May), the annualized rate of growth of both these inflation measures has plunged to 1.1% (total), and 1.7% (core). Powell's favorite measure, PCE core services less shelter, is up at a mere 1.1% annualized pace in the past 3 months. Note: these same three months include the impact of Trump's higher tariffs—which is to say that higher tariffs have not resulted in higher inflation by any measure. This is what I and many others predicted.
Chart #5
Chart #5 shows the three components of the PCE deflator: services, durable goods, and non-durable goods. As should be obvious, goods prices have been flat to down for the past 3 years. Inflation is only to be found in the services sector, and shelter costs make up a large portion of that sector. Lower housing costs are going to be depressing services inflation for a long time. The Case/Shiller index of national home prices peaked earlier this year and has fallen at an annualized rate of 1.8% in the most recent 3 months. Add it all up and the outlook for inflation is LOW for the foreseeable future. I think the Fed is getting very close to realizing this, so we will soon have lower interest rates and that should help.
Despite this somewhat downbeat, near-term outlook, I remain reasonably confident that we can avoid a disaster and the economy can improve with time. Trump has been a wrecking ball in many ways, which is unfortunate, but in the process he has provoked a lot of thought and shaken up things that needed to be shaken up (corruption and waste in the federal government, immigration, trade barriers, to name just a few). Between the Abraham Accords and the targeted bombing of Iran's nuclear sites, he may well have transformed the future of the Middle East for the better.
Friday, June 13, 2025
Household Net Worth update
Here's a quick update of charts I've been posting and writing about for a long time using recently released data for Q1/25. For more commentary, see here. The U.S. economy is an astounding engine of growth and prosperity, no doubt about it.
Chart #1
Chart #2
Chart #3
Chart #4
Wednesday, June 11, 2025
Memo to Fed: lower interest rates are overdue
In the past (before the Fed adopted an abundant reserves policy), such mistakes had severe consequences: once policy became tight enough to slow the inflation fueled by a delayed response to higher inflation, the economy invariably suffered a recession. Today it looks like we will avoid a recession, but that doesn't ensure we won't see some housing market turmoil. Liquidity in the housing market is terribly low and prices are unsustainably high, all on top of a surging inventory of homes for sale. And to the chagrin of would-be home buyers, 30-yr mortgage rates are hovering just under 7%—which equates to a crushing real interest rate of about 5% per year. If Fed policy had been more responsive in the past decade to swings in inflation, mortgage rates today would be far lower.
Meanwhile, in the good news column, today's May inflation report showed that consumer prices on average rose a mere 0.1% in May, and are up only 2.4% in the past year. However, excluding shelter costs (which are now widely understood to be a seriously lagging statistic that effectively overstates current inflation), the CPI is up only 1.5% in the past year. Abstracting from shelter costs, consumer prices have risen at a 1.8% annualized rate for the past two years. In other words, inflation has been below the Fed's target for a full 2 years. Long-time readers will know that I first made this point two years ago.
Memo to Fed Chair Powell: lower interest rates are not only justified but long overdue.
Chart #1
Chart #1
Chart #1 illustrates the relatively large gap between headline inflation and inflation ex-shelter costs. This gap has been narrowing for the past two years (though the narrowing has been slower than I thought it would be). Excluding shelter costs, consumer price inflation has been less than 2.0% year over year in 19 of the past 24 months; on an annualized basis, ex-shelter inflation has been 1.8% over the past two years.
Chart #2
Chart #2 shows the portion of the CPI that corresponds to shelter costs: Owner's Equivalent Rent makes up about one-third of the CPI. Shelter cost inflation by this measure has been declining for over two years.
Chart #3
Chart #3 shows how the year over year change in housing prices 18 months ago feeds into the OER component of today's inflation. (I have shifted the red line 18 months to the left to show this.) The most recent evidence of housing prices shows that in most areas of the country, home prices are roughly flat to down. This all but ensures that the OER component of the CPI will subtract meaningfully from consumer price inflation for the next year or two.
P.S. The FOMC meets next Wednesday, so that's the earliest we could see a rate cut. However, the market is betting that there is almost no chance the Fed will lower rates next week. The market is not expecting any cuts until the September 17 FOMC meeting, and only a 20% chance of a cut at the July 30 meeting. That seems like an awfully long time to me.
Friday, June 6, 2025
Jobs growth is moderate but likely to slow
Anyone who has followed the monthly jobs numbers for a few years knows that they are volatile and subject to significant revisions from time to time. I've tried to correct for this by stepping back and trying to see the long-term trends and whether they are changing.
As this chart shows, private sector jobs (the ones that really count) have been growing at an annual rate of a bit more than 1% for most of the past 18 months. Over the past decade, private sector jobs have grown at an annualized rate of 1.3%, while real GDP growth has been about 2.3% per year. So what we are seeing today is roughly par for the course; nothing to get excited or worried about. Except that the number of immigrants entering the labor market is in the process of slowing rather dramatically, thanks to Trump's closed borders and aggressive efforts to deport illegals. My back of the envelope calculation says that without any meaningful policy changes, jobs growth is going to slow to somewhat less than 1% a year—possibly to as low as 0.6% a year by the end of this year. This is going to leave us with an economy that struggles to grow 2% a year.
This is not the stuff of booms. For a booming economy we need to see significant reductions in tax and regulatory burdens. Fortunately this is something that Trump is working hard to achieve, so there is hope for a better economy in the years to come.
Monday, June 2, 2025
Inflation pressures were tamed a few years ago
Chart #1
Chart #1 shows the total and the core (ex-food and energy) measures of the Personal Consumption Deflators. The PCE deflator is a better measure than the CPI, because the weightings of its components are dynamically adjusted to account for changes in consumer behavior. Both measures are within spitting distance of the Fed's target—the PCE deflator rose only 2.1% in the year ending April '25. The big-picture takeaway here is that the surge in inflation which occurred in the wake of the Covid crisis ended in mid-2022. It's all over but the shouting.
Chart #2
Chart #2 shows the three major components of the PCE deflator. Note that durable and non-durable goods prices have been essentially flat for the past 2-3 years. In particular, raw industrial commodity prices are unchanged since October '22, while most commodity indices exhibit similar behavior, with the exception of energy prices, which have fallen significantly since mid-2022. Inflation is an issue only in the service sector, and those prices are dominated by wages and shelter costs, both of which tend to be lagging indicators of inflation pressures on the margin. Meanwhile, we know that housing prices continue to soften, and with only moderate increases in the money supply, it is likely that wage pressures will soften as well.
Tuesday, May 27, 2025
Survey of key market fundamentals
So far, the year 2025 has been pretty wild, not least because of Hurricane Trump. I'm not the only pundit that has been struggling to make sense of things. Seven weeks ago global markets were staring into the abyss, reeling from Trump's tariff onslaught. Some degree of calm has since been restored, and even Trump is licking his wounds.
So it's time to take a step back and survey the landscape of market fundamentals as they appear in the 11 charts which follow. With the exception of the first, all are based on variables that are driven by the interaction of market forces, rather than forecasts or policy prescriptions. Think of them as market "tea leaves" that tell a story if you know how to interpret them. The story as I see it is reasonably healthy.
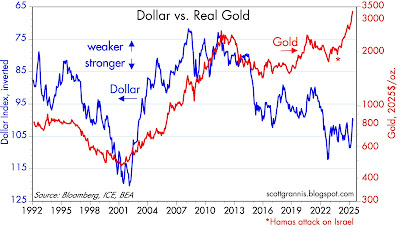
Chart #1
Chart #1 shows the level of bank reserves, which the Fed creates whenever it buys mortgage-backed and Treasury securities. Prior to the end of 2008, bank reserves were measured in tens of millions of dollars; today they are orders of magnitude higher, being measured in trillions of dollars. Prior to 2008, banks were required to hold reserves (which were non-interest-bearing) at the Fed in order to collateralize their deposits. The Fed controlled short-term interest rates and the money supply by keeping the amount of reserves relatively scarce, thus forcing banks to borrow reserves if they wanted to increase their lending.
Today, in contrast, reserves are abundant and the Fed controls short-term interest rates by paying interest on reserves. Not only are reserves now abundant and interest-bearing, they are risk-free in the bargain, making them a very attractive asset. Flush with reserves, bank balance sheets are relatively strong and the banking system has plenty of rock-solid liquidity. Gone are the days when the Fed drained reserves from the system in order to force interest rates higher, while also restricting liquidity. Abundant reserves could well explain why the economy has avoided a recession even as the Fed has tightened monetary policy.
Chart #2
Chart #2 shows the level of 5-yr Credit Default Swap spreads. This is arguably the best and most liquid measure of the market's confidence in the outlook for the economy and corporate profits (lower spreads being good, and higher spreads bad). When investors worry about the future, they demand higher spreads (the difference between the yield on corporate bonds vs. the yield on Treasuries) to compensate for uncertainty. Today, credit spreads are only modestly elevated, which means that the market is reasonably confident in the outlook for the economy and corporate profits. Spreads today are nowhere near the levels we might expect to see if the economy were teetering on the edge of recession. Chart #3 tells the same story, using an average of the spreads on all corporate bonds.
Chart #3
Chart #4
Chart #4 shows a measure of how much financial risk is being held by the private sector: it's the ratio of total household liabilities divided by total household assets. Private sector leverage today is an order of magnitude less than it was at its peak in 2008. This makes the economy much more resilient and able to withstand unexpected stresses. Thank goodness we have a prudent private sector to help offset our profligate public sector.
Chart #5
Chart #5 compares the level of the S&P 500 with the implied volatility of equity options. The latter is a commonly referred to as the "fear" index. Note how spikes in the fear index tend to coincide with declines in the stock market. As Hurricane Trump recedes from the headlines, fears are declining and stocks are advancing.
Chart #6
Chart #6 compares the level of real short-term interest rates (blue line) with the slope of the Treasury yield curve (red line). Note the strong tendency for recessions to be preceded by high real interest rates and inverted yield curves, both of which are the direct result of Fed monetary policy tightening actions. Those conditions have prevailed for the past several years, and so it is little wonder that there have been many predictions of imminent recession. I think we have avoided a recession this time thanks to the Fed's abundant reserves policy, as well as to the private sector's lack of appetite for leverage.
Chart #7
Chart #7 compares the level of real and nominal 5-yr Treasury yields to the difference between the two, which is the market's implied expectation for the average annual inflation rate over the next 5 years. Inflation expectations are reasonably stable these days and within spitting distance of the Fed's target. But ideally, I would prefer to see the Fed target zero inflation. A rock-solid currency is the best platform for a strong economy.
Chart #8
Chart #8 compares the real yield on 5-yr TIPS (red) to the ex-post real yield on risk-free overnight yields (blue). Real yields on TIPS are determined by expectations for Fed tightening. That the two are roughly identical suggests the market sees Fed policy as being relatively stable at current levels for the foreseeable future.
Chart #9

Chart #9 compares the strength of the dollar vis a vis other major currencies (blue) to the price of gold in constant dollars (red). (Note: a falling blue line represents a stronger dollar, and a rising blue line a weaker dollar.) Traditionally, gold has acted as a hedge against a declining dollar, as can be seen by the action from 1992 through 2015—a stronger dollar coincided with lower gold prices, and a weaker dollar coincided with rising gold prices. In recent years, however, this relationship has completely broken down, with gold reaching new highs even as the dollar has been relatively strong. I'm not sure what this means, but it certainly implies that gold is very expensive from a long-term viewpoint.
Chart #10
Chart #10 is constructed in a similar manner to Chart #9. It shows that until fairly recently, commodity prices (excluding oil, which is by far the most volatile of all commodity prices) have moved inversely to the strength of the dollar. I would venture to say that commodity prices look relatively expensive given the dollar's strength.
Chart #11
Chart #11 shows that real oil prices, like most commodity prices, show a strong tendency to move inversely to the strength of the dollar, even in recent years. The chart further suggests that oil is appropriately priced today given the strength of the dollar.
Wednesday, May 14, 2025
M2 charts look good
This blog is one of the few places you will find information about the all-important M2 measure of the US money supply. I've been covering this since I first began this blog in the summer of 2008. The reasons that few follow M2 are several: 1) the Fed apparently pays no attention to the money supply, 2) not many Wall Street analysts pay attention to M2, and 3) making sense of money supply is difficult in the absence of any concrete measures of money demand. I try to fill in those gaps.
These links will take you to a more in-depth discussion of this topic, but to simplify: Inflation happens when the supply of money exceeds the demand for it. M2 is arguably the best measure of money supply. Currency is arguably a proxy for money demand, as is the ratio of M2 to nominal GDP. The reason surging money supply in 2020 through early 2022 didn't create inflation is that money demand also surged. The reason that declining money supply over the past two years has not been deflationary is that money demand also declined. Today, money supply and money demand appear to be in balance, which explains why inflation has been relatively low and stable.
Chart #1
Chart #1 shows the level of the M2 money supply. M2 grew at about a 6% pace from 1995 through 2019, a period characterized by relatively low and stable inflationm which further implies that money supply and demand were in balance. M2 then exploded from March 2020 through early 2022, but inflation started rising in early 2021; this implies that money demand started to collapse in early 2021. For the past year or so, M2 growth has picked up but inflation has slowed, which implies that money demand has begun to stabilize at a lower level (see Chart #2).
Chart #2
Chart #3
Chart #3 shows currency in circulation (a lot of which is held overseas, by the way). I have argued that currency is a proxy for money demand because people only hold currency if they want to; unwanted currency can simply be deposited in a bank, whereupon it disappears from circulation and is returned to the Fed. Like M2, currency increased at about a 6% annual rate from 1995 through 2019. It then surged over the next year or so, even though we saw relatively low and stable inflation. The growth of currency then began to slow (and inflation to pick up) in early 2021, and has now returned to its long-term growth path, coinciding with relatively low and stable inflation.
In sum, money supply appears to be growing at a moderate but sub-normal rate, while money demand appears to be somewhat soft. That's not a recipe for rising inflation, and instead signals, in my view, that inflation will remain low and relatively stable for the foreseeable future.
Tuesday, May 13, 2025
April CPI looking good
A quick update to my favorite CPI chart, following today's release of the April numbers:
It's worth noting also that the April figures included the impact of some of Trump's tariffs, which resulted in higher prices for some imported goods. But this upward nudge to inflation was fully offset by a slower rise in prices for services. Which further illustrates how, when monetary policy is doing a good job, rising prices for some things are perforce offset by lower prices for others.
Wednesday, April 16, 2025
More on Trump's terrible tariffs
Here is a must-read article on the folly of Trump's tariff policy: Trump’s Tariffs Are as Bad as Bidenomics, from the April 15, 2025 edition of the WSJ.
Key excerpts:
The logic of the Trump protectionist policy is that a nation can become richer by producing at home products that it could buy more cheaply abroad. Not only does this defy reason, but the administration has presented no evidence showing how the U.S. or any other nation has benefited economically from broadbased protectionist policies.
The president’s trade policies focus exclusively on manufacturing, never mentioning America’s massive surplus in the services sector, where wages are now on average higher than in manufacturing.
In 2018, Mr. Trump imposed tariffs on washing machines, raising the cost consumers paid for these appliances by more than $1.5 billion annually while bringing in only $82 million in customs revenue. Even after netting out the tax revenue, the average annual cost to American consumers of each job created by these tariffs was north of $815,000, roughly 19 times the average annual salary earned in 2018 by production-line workers employed in manufacturing appliances.
-------------
Blogging will be light for the rest of the month since I am spending some time Italy.
Thursday, April 10, 2025
Trump's Tariffic Mistake
I'm a fan of nearly everything Trump has done this year, with the exception of his Terrible Tariffs. As I and many others have explained, Trump's threat to raise tariffs is a terrible idea because they're meant to fix something that isn't broken (Trump's claims to the contrary notwithstanding).
Our trade deficit with China, for example, means that we buy more goods and services from China than they buy from us. The difference, termed the trade "deficit," is evidence, in Trump's mind, that China is "ripping us off." But by the laws of commerce, he who sells more goods and services than he buys must do something with the net amount of money he receives. In the case of China-U.S. trade, the dollars China earns from its commerce with the US must inevitably find their way back to us in the form of investment, security or bond purchases, or simply bank deposits. Simply put: you can't spend dollars in China.
China is not ripping us off because it already spends everything it earns from our trade deficit. In economic jargon, the deficit in goods and services we have with China is completely offset by a surplus in our capital account.
Where Trump has a legitimate beef with China and other countries is their use of tariffs to make US goods and services expensive and thus reduce their demand for our stuff. They would be better off—and so would all of us—if no one used tariffs. Free global trade is nirvana for everyone. Everyone wins when tariffs are zero.
Trump understood this back in 2018 when he said during a discussion with G7 leaders that all countries should eliminate tariffs and subsidies, because that would be "true free trade." Has he forgotten what he once believed in and fully understood?
You might think so after living through the global financial turmoil of the past week or so. It was a nightmare scenario. Trump was a madman determined to wreak havoc among global economies and global trade. I was so anguished I could only think that the prospects were so awful that Trump would be forced to back off. This couldn't go on. And suddenly, yesterday, it didn't. Trump gave everyone except China a 90 day reprieve and markets rejoiced. Today, however, second thoughts were creeping back in.
I agree with what Bill Ackman said yesterday. By waiting until panic set in before announcing a reprieve, Trump forced the world to see first-hand what the results of a global tariff war would lead to. And he also put tremendous pressure on China, the biggest bad actor of global trade, to change its ways. It was a master-stroke of persuasion. Until yesterday I had begun to fear that Trump was making a huge mistake. Now my fears have been assuaged. We're not out of the tariff woods yet, but the prospects for a favorable resolution have improved dramatically. Maybe those tariffs Trump threatened weren't so bad after all, if they help the world understand how bad they can be.
Now let me comment briefly on today's CPI release, which was a pleasant surprise. The chart below says it all:
Chart #1
Chart #1 compares the year over year change in the CPI index with the same change in the CPI index ex-shelter. The ex-shelter version of the CPI has increased by 2.3% or less for the past 23 months (since May 2023), and it has averaged a mere 1.7% per year for almost two years. In the past year, ex-shelter inflation was only 1.5%. Only shelter costs have kept the broader CPI from long ago meeting the Fed's objective, and their impact is continuing to fade away.
To repeat what I said months ago, tariffs don't cause inflation. Only monetary policy causes inflation. So far the Fed has been doing a pretty good job of neutralizing the monetary excesses of 2020 and 2021.
Chart #2
As Chart #2 shows, the M2 measure of the money supply is within shouting distance of the long-term trend growth that prevailed from 1995 through 2019. Excess money has all but disappeared, and Chart #1 goes a long way to proving it.
UPDATES (4/23/25):
The March data on M2 continue the trend described above. M2 is basically unchanged over the past three years, and is up at a modest rate of 4.1% over the past year. Excess money has been drained from the economy. Credit spreads have backed off from their recent highs and are far short of flashing even a modest yellow signal. Bank reserves remain abundant ($3.45 trillion) and the Fed is no longer threatening to make them scarce.
Trump got schooled by the market, so now he's dialing back his tariff threats. This is very good news. Tariffs are taxes, and nobody needs higher taxes right now. Paring back spending by streamlining our bloated bureaucracy is the best way to fix what's wrong with the economy. Let's do more of it.
Meanwhile, I won't feel comfortable until Stephen Marin, Trump's Chairman of the Council of Economic Advisers, and Peter Navarro, his tariff-loving trade advisor, are banned from the White House. Both advocate industrial policy on a global scale (e.g., devalue the dollar to promote US exports, and jack up tariffs on countries that don't buy enough of our goods) that has NEVER worked anywhere for anyone.
I would also like to see gold fall back to $2,500/oz. The current level of $3,300 is just way too high, reflecting extreme levels of discomfort and fear that are incompatible with a healthy economic environment.
Thursday, March 13, 2025
Inflation update
Markets are in correction territory, and the economy is flirting with a recession. There's a lot of concern about the impact of Trump's beloved tariffs, and the judicial system, with the help of a weakened Democrat Party, is trying its darnedest to stymie Trump's efforts to put the federal Leviathan on Ozempic.
In any event, I detect no reason to worry about inflation. I do worry because emerging economic weakness stems from several sources: the fallout from DOGE cutbacks, the fallout from tariff wars, and the ongoing weakness in the housing market coupled with unsustainably high prices and mortgage rates. Another factor may be due to the uncertainty surrounding whether Trump's 2017 tax cuts will be extended prior to year end, when they are scheduled to revert to much higher levels. Worry about growth, not inflation.
Chart #1
Chart #1 compares the year over year change in the CPI index with the same change in the CPI index ex-shelter. It's important to note that the ex-shelter version of the CPI has increased by 2.3% or less for the past 22 months (since May 2023). Only shelter costs have kept the broader CPI from long ago meeting the Fed's objective. And their impact is almost certainly fading away.
Chart #2
Chart #2 focuses narrowly on the rate of inflation in shelter costs. The one- and three-month annualized rates of increase in shelter costs have been declining since mid-2023, and the decline looks set to continue. As it continues, and without any help from the Fed, the gap between the CPI and the CPI ex-shelter (Chart #1) will also decline, and eventually approach zero. We just need to be patient. The decline in shelter cost inflation has taken quite a few months longer than I expected, but nevertheless it is occurring.
Chart #3
Today we learned that the Producer Price Index for Final Demand was unchanged in February, but is still up 3.2% over the past 12 months. Is this a problem? I've always paid more attention to the broader Producer Price Index for Finished Goods, and it has been quite well behaved, as Chart #3 demonstrates. Both the total and core versions are up only about 2% over the past year. More impressive, however, is that the PPI Finished Goods index has only increased by 1.3% since June 2022. That's an annualized rate of increase of only 0.04% over the span of 32 months. PPI inflation is on life support.
If we can make it to year end while avoiding a massive tax increase and runaway tariff wars, the long-term effects of Trump's (stupid) tariff wars and DOGE's cost- and regulation-cutting efforts should be very positive.
Wednesday, March 5, 2025
Near-term gloom, long-term boom
Sorry for my prolonged absence. I had some minor health issues that are now behind me, and more recently I've enjoyed a few weeks skiing at Deer Valley with my brother. What's really kept me off balance, though, is the blizzard of executive orders emanating from the Trump White House—most of them good, but some—particularly punitive tariffs—bad for growth. Trump can't change so many things without causing near-term problems, even if the long-term result is undeniably positive. So I struggle to understand how serious the negative fallout of cutbacks, firings, and tariffs will be over the near term, as compared to the hugely beneficial effects of sharply reduced tax and regulatory burdens over the long term and how both those factors will play out in the months ahead. For that matter, I doubt whether anyone has a clear view.
As we continue to try to parse the daily barrage of news, there are disturbing signs that the economy has entered a weak patch. The Atlanta Fed's GDP Now model is forecasting Q1/25 growth to be a very disappointing -2.8%, driven primarily by the assumption of an import surge driven by attempts by businesses to avoid future tariffs. The housing market is fragile and housing starts are weak because prices are high and interest rates are high, and the combination renders housing unaffordable for most. Loan delinquencies are still relatively low, but clearly rising. Business capital spending has stagnated for years, but shows some signs of life of late. Meanwhile, tariffs—which are equivalent to a tax hike, and as such will disrupt sectors of the economy to some degree—are increasingly taking center stage, enough so to keep the market and the economy off balance. Private sector jobs growth is modest, while public sector jobs growth will certainly weaken thanks to DOGE house cleaning. The dollar is quite strong, and that is keeping pressure on commodity prices. The Fed is reluctant to ease further because they feel Trump's tariffs could be inflationary, and they are unwilling to overlook the fact that the CPI is a little on the high side mainly because of the way shelter costs are measured.
On the positive side—and this has been a big positive for a long time—liquidity conditions are healthy and credit spreads remain quite low. It's hard to overstate how important it is for financial markets to be free of the liquidity squeeze which has accompanied every Fed tightening episode prior to the current one. Banks are flush with over $3 trillion of reserves, instead of being forced to bid for scarce reserves. Credit markets are thus well-oiled and able to fulfill their role as a shock absorber for the physical economy; risk is able to be distributed from those who don't want it to those who do, and that is a big positive. Meanwhile, real interest rates on 5-yr TIPS have dropped by an impressive two-thirds of a point so far this year. This foreshadows a meaningful relaxation of monetary conditions which will help ease the pain in the housing and commodity markets—but not soon.
Stepping back from markets and the economy, I see a serious potential threat in the cryptocurrency space. Speculative fever is raging, turbo-charged by the belief that Trump will buy a mountain of bitcoin for a U.S. reserve stockpile—a move I consider foolish to the extreme. Some amazing statistics: there are over 10,000 different crypto currencies that now have a total market cap of $2.95 trillion, down some 20% from an all-time high of $3.72 trillion in mid-December. Bitcoin dominates, representing about 60% of the total. No one has the slightest idea of the inherent or intrinsic value of crypto currencies, so their price is driven solely by speculative ebbs and flows. Did you hear about the guy who lost a hard-drive containing $775 million worth of bitcoin and has no hope of recovering it?
A series of charts follow that help illustrate some of the above points.
Chart #1
The M2 measure of the money supply is the most important financial variable that almost no one (including the Fed) pays any attention to. (I have been reporting on M2 ever since this blog started back in 2008.) By now everyone knows that the big inflation we suffered in 2021 and 2022 was caused by a $6 trillion explosion in the M2 money supply, which in turn was fueled by $6 trillion of federal stimulus checks that were effectively monetized.
As Chart #1 shows, M2 today is only about $1.5 trillion above where it would have been if nothing extraordinary (like Covid) had happened. From 1995 through 2019 M2 grew by about 6% per year, and inflation was not a problem. M2 is now almost back on track, and inflation is no longer a problem. The Fed has tightened enough, and most of the excess money that was printed has been absorbed by the economy. This is very good news from a monetarist perspective; without excess money there can be no rise in inflation.
Turning to the economy, Chart #8 shows two measures of the growth rate of private sector jobs. Jobs growth has weakened significantly in recent years, and is now only slightly more than 1% per year.
Chart #2 tells the part of the monetary story that almost no one hears: the demand for money, expressed as the ratio of M2 to nominal GDP. When the money supply exploded in 2020 and early 2021, it wasn't inflationary because the demand for money also exploded—people let the checks sit in their bank accounts because of great uncertainty and the inability to do anything. But beginning in early 2021 the demand for money started to decline as economic life began to return to normal, and that meant the economy was suddenly holding a lot more money than desired. People began to spend that money in earnest, despite supply bottlenecks, and that quickly resulted in higher prices. Today the demand for money is almost back to where it was pre-Covid and it appears to be stabilizing, plus bottlenecks have disappeared.
Chart #3
Chart #3 shows the trade-weighted and inflation-adjusted value of the dollar vis a vis two baskets of other currencies. By either measure, the dollar today is quite strong from an historical perspective. A strong dollar is a good thing: 1) it confirms the absence of excess money, 2) it reflects confidence in the Fed and the economy, and 3) it keeps prices of imports relatively low. From a macro perspective, a strong currency is the very antithesis of inflation.
Chart #4
Chart #4 shows one reason the dollar is strong: real yields (the yields that really count) are relatively high. Real yields in turn are a good barometer of how tight monetary policy is. High real yields reflect tight money and they make owning the dollar attractive because they enhance the real return on holding dollars.
Chart #5
Chart #5 shows that commodity prices tend to move inversely to the value of the dollar (note that a rising blue line represents a falling dollar and that tends to correspond to rising commodity prices). In recent years that relationship has weakened, but it still looks to me like a strong dollar is exerting downward pressure on commodity prices.
Chart #6
Chart #6 shows the real (inflation-adjusted) price of gold from 1947 (when it was about $35/oz.) through today. I've used the Consumer Price Index to calculate how much in today's dollars it would have cost to buy gold at different times in the past. Note the enormous volatility of real gold prices. From a high of over $2,500/oz in late 1980, real prices subsequently fell to a low of $470 in early 2001—a decline of over 80%. Today, real gold prices are at all-time highs.
A century ago, an ounce of gold cost a little less than $21. Since then, the gold price has risen by 13,800%, to $2,925/oz. as I write this. Over that same hundred years, the Consumer Price Index has increased by 1,755%, which means the real price of gold has increased by 670%, or about 2% per year. Yes, gold tends to hold its value over time, but sometimes it takes a lifetime for that to be true.
Chart #7
Chart #7 compares the dollar to real gold prices. Here we see that from 1997 through late 2022 gold has shown a strong tendency to rise as real yields fall and to fall as real yields rise (note that real yields are plotted on an inverse scale), and vice versa. That makes sense because high real yields are a compelling alternative to owning gold, because TIPS not only preserve purchasing power but they also offer positive income, whereas gold only sometimes preserves its purchasing power and pays no income. But in the past several years the opposite has happened: gold has risen as real yields have risen!
That gold, bitcoin and the dollar today are all historically strong, at a time when real yields are relatively high and the dollar is strong, demands a closer look. In theory, gold should rise in dollar terms as the value of the dollar falls, and gold should fall in dollar terms as the dollar rises. Meanwhile, the dollar tends to rise as real yields rise.
Chart #8
Chart #10
Chart #10 shows the nominal and inflation-adjusted value of national home prices since 1987. Real home prices are at all-time highs by a clear margin, but they haven't increased for the past several years.
Chart #11
Chart #12
Chart #13
Chart #13 compares an index of builder sentiment to the level of housing starts. Builder sentiment has been depressed for several years now, likely because of how unaffordable homes are. Until this improves, the level of housing starts is likely to remain depressed as well. That in turn will only aggravate the picture, since a dearth of new homes will tend to put upward pressure on housing prices. The solution to this must come in the form of lower interest rates and/or rising incomes and/or lower home prices.
A final thought: a reasoned calculation of the amount of federal, state, and local government fraud approaches the staggering sum of $1 trillion per year. Meanwhile, I can't pretend to know how the blizzard of activity in Washington is going to affect the economy over the next 3-6 months. We could easily see a mild recession, but would that justify a bearish investment stance?
I remain an inveterate rational optimist: there are so many things that could be fixed for the better in this country!
Happy Hunting, Elon!
Friday, January 10, 2025
Tariff fears trump modest jobs growth
Today's December private sector jobs report beat expectations (223K vs. 140K) and that supposedly triggered a sharp, negative response from the bond market. Interest rates are now priced to only one more cut in the Federal funds rate for the rest of this year. As a result, in the past few months short-term interest rates have jumped by almost one percentage point, 10-yr Treasury yields have jumped by more than one percentage point, and 30-yr mortgage rates have risen to almost 7%.
But the perceived health of the jobs market wasn't the only thing that rattled the bond market today. Another contributing factor was the Fed's fear (shared by the market) that Trump's threatened tariffs would boost inflation, as revealed in the minutes of the last FOMC meeting. From mid-August, when Trump's probability of winning the election bottomed, 5-yr average inflation expectations have jumped from 1.87% to 2.54%. In any event, it remains the case that inflation is not caused by a stronger jobs market or stronger economic growth: growth has soundly beat expectations in recent years even as inflation has declined significantly.
Whatever the cause, higher rates and higher inflation expectations effectively put the kibosh on hopes for lower mortgage rates, and thus will likely worsen the prolonged period of historically weak home sales, housing starts, and new mortgage applications which began over two years ago. Sadly, it will add insult to the injury of many thousands of displaced Los Angeles area residents seeking to rebuild or replace homes lost to multiple fires.
As I see it, the rationale for today's sharply higher rates and slumping stock market has weak underpinnings: the mistaken belief that tariffs will boost inflation and thus require tighter-than-expected Fed monetary policy.

Chart #5 compares the level of real yields on 5-yr TIPS to an index of the dollar's strength vis a vis other major currencies. Rising real yields are an excellent measure of how tight monetary policy is. Not surprisingly, tight money and high real yields have significantly boosted the dollar's appeal. A strong dollar positively impacts our purchasing power while also keeping imported goods prices low; indeed, a strong dollar is an excellent defense against inflation, especially when accompanied by tight monetary policy.
Chart #1
Chart #1 shows the monthly change in private sector payrolls over the past 3 years. Note how volatile this statistic is on a month-to-month basis; that anyone—especially the Fed—would use just one month's number as a basis for important long-term policy decisions strains credulity. But that's what happens every now then, with today being a prime example.
Chart #2

Chart #2 uses a more realistic approach to interpreting the state of the jobs market, by focusing on percentage changes in jobs over 6- and 12-month periods. By either measure there has been a dramatic slowdown in jobs growth in recent years. At best, jobs currently might be growing at a 1.3% annual rate, which is marginally lower than the 1.4% annualized rate that has prevailed over the past 30 years (a period that includes three recessions). Current jobs growth is moderate at best.
Chart #3
Chart #10 shows the level of 10-yr Treasury yields, which is the benchmark for all long-term interest rates (including fixed-rate mortgages). Simply put, interest rates have exploded higher in recent years. Only abundant liquidity has kept this from tanking the markets and the economy. (For a longer explanation, see this post from last November.)
Chart #4
Chart #4 compares the level of fixed rate mortgages to an index of new mortgage applications (as opposed to mortgage refinancings). The plunge in new applications reflects a similar plunge in new home sales and housing starts. In effect, sharply higher rates have crushed the housing market.
Chart #5
Chart #6
As I mentioned in my last post, a strong dollar puts downward pressure on commodity prices. Indeed, industrial commodity prices have declined in both real and nominal terms over the past two years, as shown in Chart #6, thanks to a strong dollar.
Monetary policy is tight and has become tighter of late, as the market and the Fed worry about the presumably inflationary impact of Trump's tariffs that have yet to be imposed. It makes much more sense to believe that Trump's promises to significantly lower tax and regulatory burdens will deliver stronger growth with low inflation.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)